Currently, mealworms are being seen as more than just pests that ruin grains due to their high protein content. Animals raised on farms and outdoor chickens are also fed mealworms, like reptiles and captive birds, as well as pets, including pets, such as reptiles and captive birds.
Humans eat farmed fish, and the byproducts of the fish are used to feed pigs and poultry by drying and processing them into fishmeal. Fishmeal is also used as a fertilizer for growing fruits, vegetables, and nuts. Our food supply chain already incorporates mealworms.
Fishmeal is also high in protein, but metals and other contaminants may be present. By raising mealworms organically, farmers can eliminate contaminants and chemicals from their diet and environment.
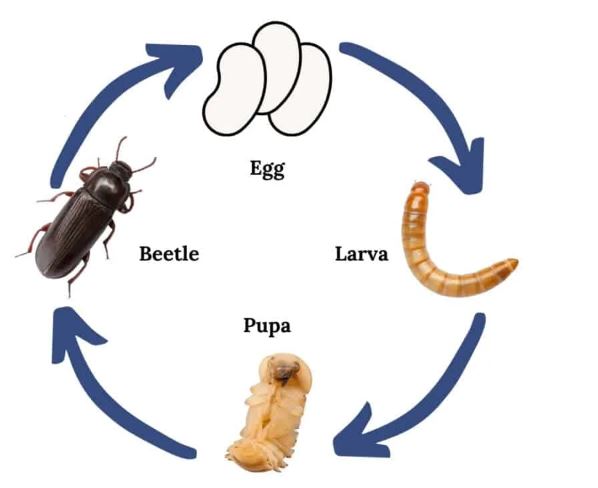
There is no such thing as a mealworm. Tenebrio molitor larvae are darkling beetles of the Tenebrio molitor species. Eggs, larvae, pupae, and adult beetles comprise the beetle’s life cycle. A larvae takes several generations to reach 2 cm or 3 cm in length, after which it undergoes a number of instars. Approximately 1.25 cm to 1.8 cm is the length of adults. A beetle’s lifespan is several months. During their lifetime, females lay around 500 eggs.
It is natural for mealworms to eat vegetation, dead insects, and their own skin casings from developmental molts. Food waste is fed to mealworms in captivity. “Mealworms, Tenebrio Molitor, darkling beetle larvae on white background.”

Cycle of life of mealworms
Darkling Beetle larvae are called mealworms.
A mealworm’s life cycle has four stages: egg, mealworm, pupa, and beetle.
Mealworms hatch from darkling beetle eggs. Mealworms grow into pupae. Darkling Beetles mature over time into pupae.