Amalki is the Sanskrit word for amla (Phyllanthus emblica). Different parts of the world call it emblic myrobalan, myrobalan, Indian Gooseberry, or Malacca tree.
Location :-
Among the largest amla-growing states in India are Uttar Pradesh and Himachal Pradesh. In Uttar Pradesh (Azamgarh, Pratapgarh, Varanasi, and Barelli districts), Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Karnataka, it is mainly grown.
Mohphology of plants:
Amla trees range in height from 3 to 26 feet 3 inches (3 to 3 feet 3 inches). There are no glabrous or finely pubescent branchlets, the leaves are simple, subsessile and closely set along branchlets, and they are light green, resembling pinnate leaves. A greenish-yellow color characterizes the flowers. There are six vertical stripes or furrows on the fruit, which is nearly spherical in shape and light greenish-yellow in color.
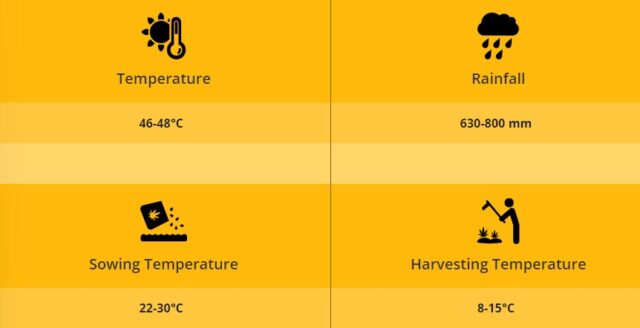
Getting ready to sow :-
Between July and September is the best time to cultivate amla. During the months of January and February, cultivation is done in Udaipur.
Getting ready to sow :-
Amla is best cultivated between July and September. The cultivation of Udaipur takes place in January and February.
Requirements for soil :-
Amla is a hard plant, so it grows well on both light and heavy soil except pure sand. Calcareous soil is suitable for growing it, as well as slightly acidic to saline soils. Fertile-loamy soil with good drainage gives best results.
Preparation for the field:-
During May-June, 1 m3 pits are dug at a distance of 4.5 m and should be exposed to sunlight for 15-20 days. Before planting the grafted seedlings, fill each pit with surface soil containing 15 kg of farm yard manure and one kg of superphosphate.
Variations:-
Among the many varieties of Amla are Banarasi, Krishna, NA-9, NA-10, Francis, NA-7, NA-6, and Chakiya. For commercial purposes, Banarasi is the most important variety.
The Seed Sowing Process:-
- Udaipur cultivates amla from July to February, while July is the month of cultivation in Amla.
- The seedlings should be sown at a distance of 5 meters x 4.5 meters in May or June.
- For exposure, 1-metre square pits are dug and left as such for 15-20 days
- Seedlings planted in the main nursery after budding
System of cropping:
Because amla trees have deep roots and sparse foliage, they are ideal for 3 or 2 tier crop systems. Amla orchards are well suited for intercropping with fruits, vegetables, flowers, medicinal plants, and aromatic plants.
Controlling nutrients :-
Soil enrichment can be achieved through the use of green manure crops. Farmyard manure has shown better response than paddy straw, sugar cane trash, and sugarcane trash. As salt-affected soils are mulched with organic waste for a number of years, their organic matter content can be significantly improved, their infiltration rate will be increased, and the movement of soluble salts will be restricted, thus avoiding their toxicity threat.
Management of water resources:
Water your trees through drips at 25-30 liters/day/tree in October-December in summer and 15 days/tree in winter. It does not require irrigation during the monsoon season. During flowering, you should avoid irrigation.
Managing weeds:
Make sure the field is weed-free by frequent weeding. It is also necessary to train and prune the animals. It is cut only 4-5 straight branches to allow for future growth after eliminating cross-branch branches.Controlling soil weeds with mulch is also an effective method. Mulching is typically done in summer between 15 and 10 cm from the trunk of the tree.
Managing pests:
The pests are:
Caterpillars that eat bark: They damage the bark and stem by feeding themselves.

Caterpillars of galls: Bore into the apical meristem and build tunnels.

The following diseases can be found:
Symptoms of internal necrosis
The main cause is a deficiency of Boron. The symptoms of this disease include browning and then blackening of tissues.

The disease is treated with boron @0.6% in September and October.
A fruit that rots:
It is characterized by swelling of fruits and a change in their color.

Borax or NaCl at 0.1%-0.5% can be applied to cure this disease.
A rusty surface
Leaves and fruits are affected by circular red rust.
Two applications of Indofil M-45 @0.3% are given. For disease control, one application is made in early September, and another one is made 15 days later.
The harvest:-
After planting, plants start producing in 7-8 years. This process takes place in February when the fruits are at their greenest and have the highest amount of ascorbic acid in them.
Result :-
It is possible for an amla plant to produce up to 200 kg of fruit per year at full maturity.


